How to Determine Which Polymer Is Used for a Molecule
M 1 M 2 M 3. The synthetic methods used to prepare this and other polymers will be described later in this chapter.

Polymerization Definition Classes Examples Britannica
A sharp molecular weight distribution peak indicates a sample that has mostly one narrow molecular range also known as a monodisperse sample.

. For example if a polymer contains 13. Spectroscopy techniques including Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy Raman spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy can be used to determine the chemical composition. M is the molecular weight of the polymer DP is the degree of polymerization and the M 0 is the formula weight of the repeating unit.
If a polymer is made from more than one type of monomer or has more than a. A polymer molecule is a molecule that contains a sequence of at least 3 monomer units which are covalently bound to at least one other monomer uni t or other reactant. Rubber for example is a mixture of polymer chains whose mass differs by a factor of 10 or more but whose average molecular weight is 100000 grams per mole.
A sharp molecular weight distribution peak indicates a sample that has mostly one narrow molecular range also known as a monodisperse sample. It is experimentally determined by measurements of the osmotic pressure of the polymer. Wide-angle X-ray scattering also called wide-angle X-ray diffraction is used to determine the crystalline structure of polymers or lack thereof.
A Depiction of a Floc Formed by a Cationic Polymer Chain Bridging the. The most accurate method for determine absolute molecular mass of a polymer is vapor pressure osmometry VPO. Each working group will need approximately 15 cm 3 of each liquid so 15 working groups might use 200250 cm 3 in total.
In the context of this definition. Introduction Synthetic polymers are polydisperse to varying degrees in a variety of ways. A broad molecular weight distribution peak indicates that there are many different molecules with different molecular weights that the sample is very polydisperse.
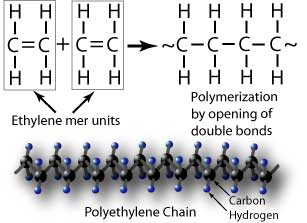
Essentially monomers are the building blocks of polymers which are more complex type of molecules. In this method the polymer should be in liquid form. Are all long carbon chains but the lengths may vary by thousands of monomer units.
Are the number of macromolecular with molecular masses. Respectively then the number average molecular masses of the polymer is given by. Molecules composed of sugar monomers.
While membrane osmometry gel permeation chromatography viscosity analysis and mass spectrometry are typically used for molecular weight determination the techniques can be time consuming inaccurate for the molecular. Updated on June 26 2019. Molecular Weight and its Distribution 1.
1 A number-average molecular weight M n. Carbohydrates lipids proteins and nucleic acids. Divide chains into series of size ranges and then determine the number fraction x i of each size range where M i represents the mean molecular weight of the size range i and x i.
MALS is used for determining the molecular size based on the fact that the anisotropic light scattering pattern produced by larger molecules of around 10 to 15 nm radius and above is associated with their size. The composition of the whole sample free of water salts and additives is defined by Acetate butyrate AGU 100. One may describe chain length in terms of polymer average molecular weight which can be defined in several ways.
The chains in a sample may differ in for example molecular weight degree of long or short-chain branching stereostructure or composition either grossly as with copolymers or slightly as with end group. M DP M0. If carefully controlled the solutions should be recoverable afterwards to be stored for reuse.
Polymer Analysis by NMR. The most common technique that is used to determine the average molecular weight of a polymer is the viscometry where Ubbelohde viscometer is employed. A monomer is a type of molecule that has the ability to chemically bond with other molecules in a long chain.
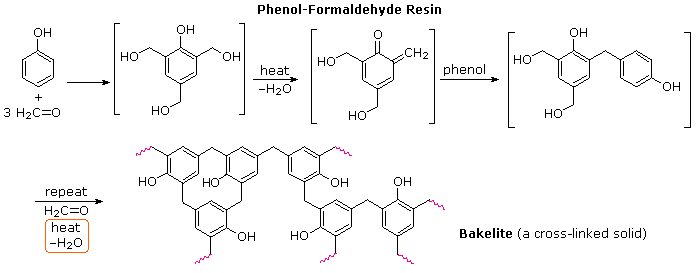
A polymer is a chain of an unspecified number of monomers. Natural rubber for example is a polymer that contains large numbers of -CH 2 CCH 3CHCH 2 - units. Details for preparing the solutions of known density are as follows for 1 dm 3 of each.
One of the challenges polymer scientists face is molecular weight avg. Measuring Molecular Size 2 - MALS. Chain length determination of their materials.
Because of this polymer molecular weights are usually given as. Unlike simpler pure compounds most polymers are not composed of identical molecules. While membrane osmometry gel permeation chromatography viscosity analysis and mass spectrometry are typically used for molecular weight determination the techniques can be time consuming inaccurate for the molecular weight ranges involved or.
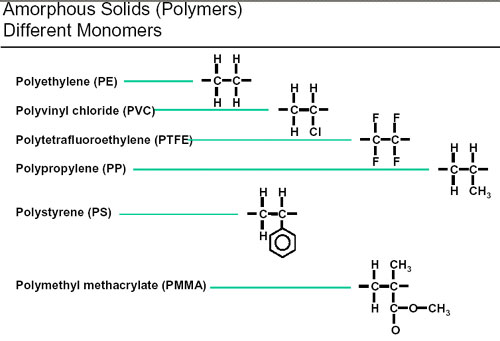
Density in gcm 3. Thus polytetra uoroetheylene is a polymer made by polymerizing tetra uoroethylene monomers. The most common technique that is used to determine the average molecular weight of a polymer is the viscometry where Ubbelohde viscometer is employed.
If not it has to be dissolved using a. For this reason MALS cannot determine molecular size for smaller molecules. Number Average Molecular Masses.
Weight Average Molecular Mass. Polymers that have a positive charge otherwise known as cationic and a high molecular weight are typically used for thickening and dewatering solids separation processes. They are necessary for energy storage.
There are four basic kinds of biological macromolecules. If N 1 N 2 N 3. The number of monomers in a polymer can differ from one chain to the next.
If a polymer is made from only one type of monomer or if it has a single repeat unit it is called a homopolymer. There are two types of average molecular masses of Polymers. The amount of polymer molecules presenting the same molecular weight must be 50 of the weight of the substance.
Number Average Molecular Masses. Polymers often indicate the starting monomer material. Carbohydrates are also called saccharides and their monomers are.
Calculate the degree of polymerization of a sample of polyethylene CH2-CH2n which has a. These polymers are composed of different monomers and serve different functions. One of the challenges polymer scientists face is molecular weight average chain length determination of their materials.
The weight-average degree of polymerization is the weighted mean of degrees of polymerization weighted by the weight fractions or the overall weight of. Polymers can have different charges charge densities and molecular weights.
Nondestructive Evaluation Physics Materials

Difference Between Polymer And Protein Structure Sequence Specificity Download Scientific Diagram
No comments for "How to Determine Which Polymer Is Used for a Molecule"
Post a Comment